
In this digital age, it is complicated to understand what you believe by watching online. Misinformation is rapidly spreading everywhere, from videos that look impossibly real to news stories that twist the truth. Deepfakes videos, images, or audio altered using AI are becoming increasingly common, and they can be used to impersonate people, spread scams, or manipulate public opinion. The scary part is how convincing they can be.
However, there is also a way to save yourself from falling into this trap. Using the right method, anyone can learn to identify manipulated content and protect themselves from misinformation. In this article, we’ll take a close look at what Deepfake photos and videos mean, where they are most often used, and the practical ways you can detect them.
What Is a Deepfake?
A deepfake is a type of synthetic media is a video, image, or audio clip, that’s been created or altered using artificial intelligence to look or sound real. The term comes from combining “deep learning” with “fake,” highlighting the AI technology behind it.
Modern deepfakes can imitate a person’s face, voice, or even movements with startling realism. Some of the most common forms include:
- Face swaps: Replacing someone’s face in a video with another person’s.
- Lip-sync deepfakes: Keeping the original face but digitally altering the speech so the mouth matches different words.
- Voice cloning: Replicating a person’s voice, tone, and speech patterns without using their face at all.
 StartupTalkyPratiksha Bajikar
StartupTalkyPratiksha Bajikar
Why DeepFakes Are Hard to Spot?
DeepFakes can look incredibly realistic. The Kaggle Deepfake Detection Challenge demonstrated just how sophisticated AI-generated videos have become, with prizes of $1,000,000 awarded to teams developing the best detection algorithms.
However, beyond machine learning, the public’s ability to spot subtle cues can play a crucial role in fighting misinformation.
How to Identify DeepFake Images and Videos Like a Pro?
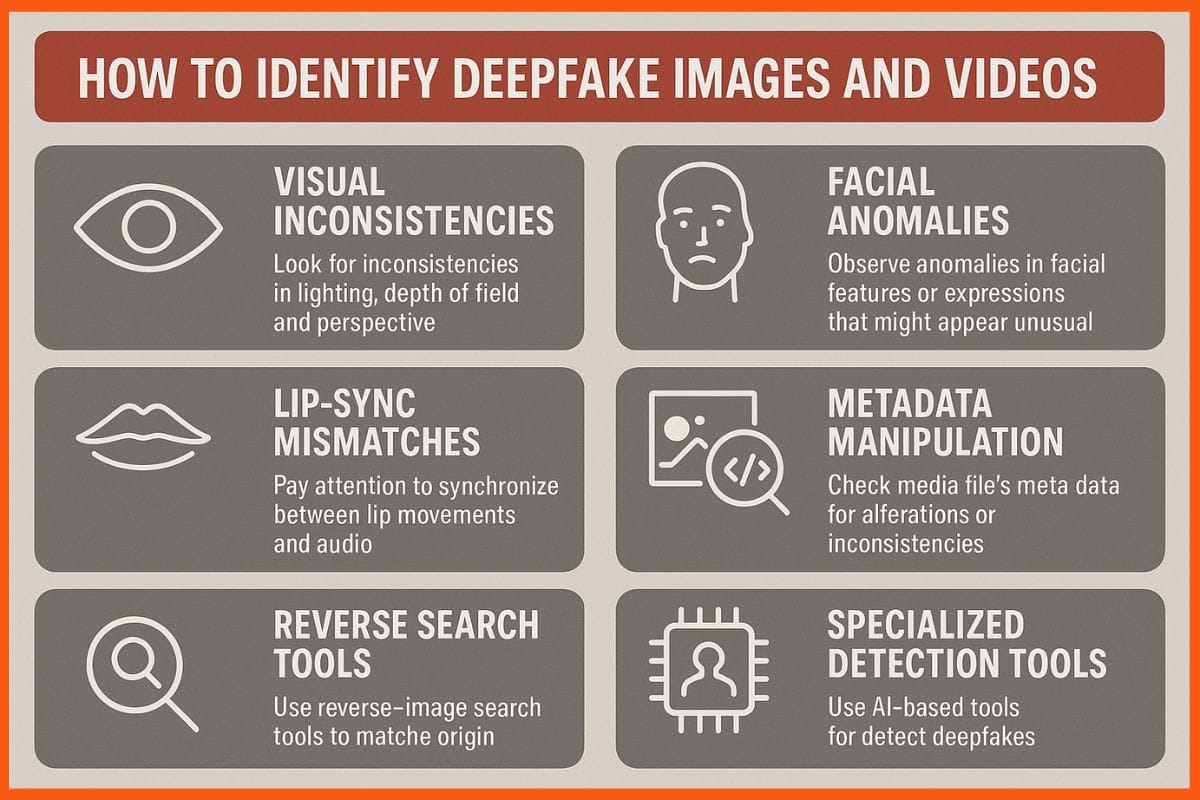
Detecting a DeepFake isn’t always easy, but there are visual, behavioral, and technical clues that can help. Here’s what to look for:
Visual Inconsistencies
Unnatural lighting, flickering edges, blurred backgrounds, or overly smooth skin can indicate manipulation. Also, watch for mismatched shadows or reflections, which AI often fails to reproduce accurately. Small distortions in the background or objects may further reveal that the video has been altered.
Facial Anomalies
Misaligned eyes, distorted teeth, unusual blinking, or inconsistent aging between facial features are common giveaways. Pay attention to subtle asymmetries in the face, such as uneven lips or jawline changes, which often appear in DeepFakes. These imperfections may not be immediately obvious, but can raise suspicion.
Lip-Sync Mismatches
When the audio doesn’t align perfectly with the mouth movements, it’s often a warning sign. Listen for unnatural pauses or timing errors in speech, and observe if facial expressions match the tone and emotion of the voice. Inconsistencies here are common in AI-generated videos.
Facial Hair, Moles, and Details
Facial hair may look unnatural, or moles and freckles may shift inconsistently. Check whether beards, sideburns, or mustaches appear patchy or blurry. Tiny features like blemishes, scars, or beauty marks may also move or change shape unnaturally.
Metadata Manipulation
Check file creation and modification dates. DeepFake tools often alter or erase metadata, leaving behind inconsistencies. If metadata seems missing or contradictory, it could indicate that the video was exported or tampered with multiple times. Comparing metadata across similar files can reveal suspicious discrepancies.
Reverse Search Tools
Use TinEye or Google Image Search to track original images or video thumbnails. If a similar video exists elsewhere with different content, it’s likely a fake. This can also help identify if a frame from a video has been reused in a different context, a common tactic in misinformation campaigns.
Specialized Detection Tools
Free browser plug-ins like DeepFake-o-Meter or AI platforms like Microsoft Video Authenticator and Intel’s OpenVINO can analyze content for DeepFake artifacts. These tools can detect subtle inconsistencies that are invisible to the naked eye, such as unnatural pixel patterns, temporal inconsistencies, or AI-generated noise.
With practice, anyone can become more adept at spotting DeepFakes by paying attention to these subtle signs. Over time, combining observation skills with technical tools will significantly improve your ability to discern real from fake.
 StartupTalkyPrithvi Durai
StartupTalkyPrithvi Durai
Key AI Techniques to Detect DeepFakes
As deepfakes become more sophisticated, AI offers powerful ways to spot them. Here are the main techniques used in detecting fake media:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs analyze images by detecting edges, textures, and patterns through multiple layers. Trained on real and manipulated media, CNNs spot subtle anomalies in skin texture, lighting, facial landmarks, or blinking patterns that humans might miss. They excel at detecting inconsistencies in facial features, resolution, and reflections in the eyes.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs specialize in analyzing sequential data, making them ideal for videos. They detect irregular motion, lip-sync errors, or unnatural expressions over time. LSTM-enhanced RNNs track temporal patterns to identify inconsistencies in movements or speech.
Autoencoders
Autoencoders learn to compress and reconstruct authentic images or videos. When fed a deepfake, the reconstruction often contains subtle errors or artifacts. These discrepancies help reveal AI manipulations in pixel distributions or overall structure.
AI-Based Audio Analysis
AI can analyze voice tone, rhythm, and modulation to spot fake audio. Deepfake audio often has unnatural pitch, cadence, or breath patterns. Spectral analysis further highlights frequency or amplitude inconsistencies typical of synthetic speech.
Biometric Analysis
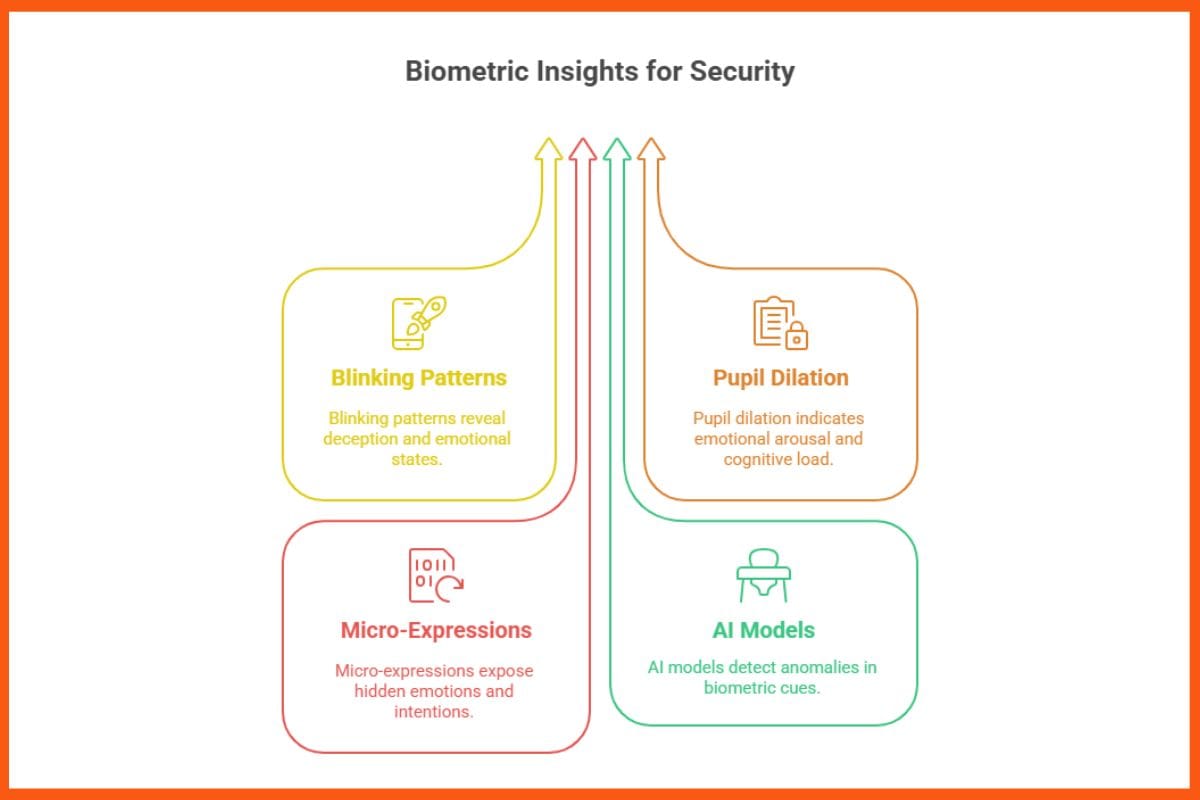
Biometric cues like blinking patterns, pupil dilation, and micro-expressions are difficult to fake. AI models can detect abnormal gaze, unnatural facial movements, or inconsistent micro-expressions, especially useful for authentication and security contexts.
Adversarial Training
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) train detection models against fake generators. The discriminator learns to identify subtle forgeries while the generator improves, creating a constantly evolving detection system that adapts to new deepfake techniques.
Forensic Analysis
AI examines digital fingerprints such as metadata, compression artifacts, and noise patterns. Irregular timestamps, abnormal pixel noise, or unusual compression artifacts often reveal tampering in images, videos, or audio.
Transfer Learning
Pre-trained AI models are adapted to detect new deepfake types quickly. By fine-tuning models on updated datasets, transfer learning allows rapid detection of emerging manipulations without starting from scratch.
Attention Mechanisms
AI models focus on high-risk areas, like eyes, mouth, or lighting inconsistencies. This targeted analysis helps detect subtle artifacts, such as mismatched reflections or shadows, that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid models combine CNNs, RNNs, and attention mechanisms for robust detection. By integrating spatial, temporal, and focused analysis, they excel at spotting complex manipulations in both images and videos, useful for news verification, legal evidence, and social media monitoring.
Conclusion
Deepfakes represent a major challenge in the digital age, but AI provides powerful tools to detect and combat this growing threat. By learning sophisticated machine learning models, we can identify and mitigate the risks posed by deepfakes, protecting the integrity of information in our increasingly digital world. As AI continues to advance, so too will our ability to detect and defend against these forgeries.
Furthermore, raising public awareness and promoting digital literacy can help individuals critically assess the content they encounter online. Collaboration between tech companies, policymakers, and researchers is essential to create effective regulations and detection standards. Ultimately, a combination of AI innovation and human vigilance will be key to maintaining trust in digital media.
 StartupTalkySubham Kumar
StartupTalkySubham Kumar
FAQs
What is a deepfake?
A deepfake is a type of synthetic media—video, audio, or image—created using AI to mimic real people or events. They often involve face swaps, lip-sync alterations, or voice cloning.
How can I spot a deepfake video or image?
Look for visual inconsistencies like unnatural lighting, flickering edges, mismatched shadows, or blurred backgrounds. Check facial anomalies such as odd blinking, distorted teeth, or shifting moles and freckles.
What are the signs of deepfake audio?
Deepfake audio often has robotic tone, unnatural pauses, or inconsistent breathing. AI-generated voices may lack natural pitch variations or emotional expressions.
Original Article
(Disclaimer – This post is auto-fetched from publicly available RSS feeds. Original source: Startuptalky. All rights belong to the respective publisher.)