
Walmart is one of the largest retail companies in the world. It was founded in 1962 by Sam Walton and has its headquarters in the United States. The company's main aim is to provide consistent discounts, loyal customer service, and fast, friendly service.
Walmart’s target is to expand its business in large cities as well as spread retail stores throughout the world. The retail stores of Walmart are divided into four divisions: Walmart Supercenters, Discount Stores, Neighborhood Markets, and Sam’s Walmart aims to expand its business in large cities and open retail stores worldwide. Its retail stores are divided into four divisions: Walmart Supercenters, Discount Stores, Neighborhood Markets, and Sam’s Club warehouses. More than 100 million customers visit these Walmart Stores.
It is very uncomfortable for small merchants and communities in America. Walmart reaches their town and provides low-cost offers and the best customer service. It is a very bad condition for small merchants and businessmen in America. To downtown merchants, Walmart just comes and takes over all the small stores.
Its purchasing power, aggressive marketing, and providing low prices to customers by Walmart, tend to pull out the business of small merchants. Gradually, the dream of the Walmart company to become the largest retailer in the world is full filing day-by-day. However, they increase their business by wrong actions and do not respect the culture or language of the communities.
This article serves as a case study of Walmart, examining its business strategies, revenue model, acquisitions, controversies, and impact on the retail market.
Timeline Events of Walmart
Walmart Business Model
How Walmart Generates Revenue | Walmart Revenue Model
Walmart Marketing Strategy
Walmart – Acquisitions
Walmart Controversies
Walmart SWOT Analysis
Walmart Future
Timeline Events of Walmart
The Timeline of events for the Walmart company since its inception.
- 1960: Sam Walton opened his first discount store in Rogers, Arkansas.
- 1981: Walmart becomes the largest company in America.
- 1981: After becoming the largest company in America, they opened their stores in a small Louisiana town.
- 1983: Walmart opened its stores in Pawhuska and Oklahoma.
- 1986: Walmart claims that it can restore more than 4000 jobs to American Communities.
- 1989: They launched a campaign about Environmental awareness that Walmart is aware of land, water, and air.
- 1990: There are some activist groups against the expansion of Walmart’s stores.
- 1990: Walmart closed its stores in Louisiana.
- 1991: Walmart opened up its store in Iowa City.
- 1998: Walmart’s founder, Sam Walton, created a family charity named Walton Family Charitable Support Foundation.
- 1999: Walmart takes over the ASDA Chain (a British supermarket chain), and now they have stores and depots across the United States.
- 2001: Walmart became the world’s largest retailer, with huge sales of $191 billion.
- 2003: Walmart opened its stores in Beijing, and now they have 22 stores in China and counting.
- 2006: Walmart closed its stores in Germany.
- 2007: Walmart is operating more than 2500 retail units in Walmart International and has more than 500,000 employees in some countries.
- 2007: By the end of this year, they had a net $45 billion in sales.
- 2008: Walmart opened its wholesale facility in India. This is the first step of Walmart's plan to sell products through its retail outlets in India.
- 2018: Walmart acquired Flipkart for $16 billion and owned a 77% stake in India’s largest online retailer brand.
- 2020: Walmart launches Walmart+, a subscription service to compete with Amazon Prime
- 2023: Expands investments in robotics, data, and generative AI to improve operations.
Walmart Business Model
There are different business models followed by successful companies, which vary from time to time. This Walmart business case study analyzes the company's strategies, challenges, and market influence, highlighting its role as a leader in the retail industry. The business model of Walmart is based on eliminating the middleman from the distribution channels. The advantage of removing the middleman is to provide benefits to the consumer by providing products at lower costs. The main motive of Walmart’s business strategy is to enter every segment of the market and dominate the market by providing products at a lower price. The Walmart case study in strategic management highlights how the company leverages its Everyday Low Prices strategy, efficient supply chain, and global expansion to maintain a competitive edge in the retail industry.
The main marketing strategy of the company is based on leading on price, being competitive, and delivering a great experience with the motto ofEveryday Low Prices.
Everyday Low Prices
Walmart’s strategy centers on offering consistently low prices across a wide range of products, from groceries to electronics, making it popular with budget-conscious shoppers who value convenience and quality. This focus on affordability gives Walmart a strong edge, especially among American consumers.
In 2017, Walmart doubled down on this approach, investing significantly in price cuts, which boosted its revenue to over $485 billion and strengthened its reputation for value. As competition heats up, Walmart stays competitive by not only keeping prices low but also improving convenience and customer service, helping it maintain a leading position in the retail market.
Walmart has three important segments mentioned below:
Walmart U.S
Walmart U.S. operates in the U.S. They provide customers with products and services that are not present physically in stores. They provide their services via the website and mobile application. The website of the Walmart company has a special feature that allows a third party to sell products. The company operates its business on various platforms like supermarkets, discount stores, neighborhood markets, and e-commerce websites.
Walmart International
Walmart International is also divided into three sections, which are retailers, wholesalers, and other small projects. These sections are also divided into various sections such as supermarkets, warehouses, electronics, apparel stores, drug stores, digital retailers, and many more.
Sam’s Club
It is the online platform of Walmart’s company, i.e., “samsclub.com”. This club consists of memberships in the only warehouse retailer operations. This section includes warehouse clubs in the U.S., as well as samsclub.com.
 StartupTalkyRoshni Tamta
StartupTalkyRoshni Tamta
How Walmart Generates Revenue | Walmart Revenue Model

In the fiscal year ending January 31, 2024, Walmart generated a global revenue of approximately $648 billion, marking a 6% increase from the previous year. Walmart has grown into one of the world’s most recognized and valuable brands, operating a network of discount stores, supercenters, and neighborhood markets across the globe.
The revenue model of Walmart deals with the principle of buying in bulk in one go. In this system, they got a huge discount from the manufacturers. They sell in small quantities at low prices. By reducing the price, they have a high sales volume, through which they have high earnings.
Walmart generates its revenue by removing the middleman and selling its products directly to customers and services to businesses. The two main sources of revenue are Product revenue and Service revenue.
Walmart's revenue in the fiscal year ending January 2024 was $648 billion.
Product Revenue
Walmart has a wide range of products in various categories:
- Grocery: In the grocery category, they have products like Daily needs products, dairy products, frozen foods, bakery, baby products, beauty aids, and many more.
- Health and Wellness: The health and wellness category has products like Pharmacy products and clinical services.
- Entertainment: The entertainment category has products like electronics, toys, cameras, movies, music, videos, and books.
- General Merchandise and Specialty Products: Stationery, paints, hardware, Automotive, sporting goods, crafts, and seasonal merchandise.
- Apparel: Apparel categories include apparel for men, women, boys, girls, shoes, jewelry, and accessories.
- Home Appliances:Home appliances include home furnishing services, home decor, living, and horticulture.
Service Revenue
Walmart also provides services to generate revenue in various fields:
- Financial Services: They provide financial services like prepaid cards, money orders, wire transfers, money transfers, bill payments, and so on.
- VUDU Movie Streaming Services: This is a subscription-based OTT platform for buying and renting movies and watching TV shows on demand.
- Clinical Services: Clinical Services include primary health care, Physical and Wellness checks, and Clinical lab tests.
- Health Insurance Services: To cater to customers’ healthcare coverage requirements.
Walmart Marketing Strategy
Walmart's Business Strategy Analysis is one of the most important parts of any business, whether it is small or large. This Walmart marketing strategy case study explores the company’s approach to pricing, promotion, and customer engagement. It is very important to make an effective marketing plan to survive in the market. Walmart uses the principle of business marketing penetration method, which is used to capture the market by offering lower prices and competitive prices to the consumers.
The company follows cost leadership, which makes a huge profit for the company. The company provides low prices to the consumer and treats all the customers as king of the market to maintain the relationship between Walmart and the customer.
According to Walmart, four factors drive the customer’s choice of retailer:
- Price
- Access
- Experience
- Assortment
One more reason for the success of Walmart is purchasing products from local manufacturers in bulk in one go and selling them in small quantities. Buying from local manufacturers is a benefit for both. Buying more products from local manufacturers means they are creating more jobs and reducing the unemployment rate. They should provide good quality products at a lower price to maintain a good relationship with customers and continue to make profits in business.
 StartupTalkyArchana Karthikeyan
StartupTalkyArchana Karthikeyan
Walmart Acquisitions
Acquisition of Jet.com

In 2016, Walmart bought Jet.com to boost its online shopping and compete with Amazon. Jet.com’s founder, Marc Lore, joined Walmart’s leadership and brought strong e-commerce experience.
With Lore’s help, Walmart improved its online business, bought brands like Bonobos and Moosejaw, and used Jet.com’s tech and data tools to make its supply chain better and understand customers more.
This move helped Walmart grow faster in the digital space and attract more young, urban shoppers. It also showed Walmart’s serious push to become a strong player in e-commerce. Though Jet.com was later shut down, its impact on Walmart’s online growth was long-lasting.
Walmart-Flipkart Acquisition

Flipkart is one of the leading Indian e-commerce brands. In 2018, Walmart took a 77% stake in India’s largest e-commerce company, Flipkart, and made the world’s biggest purchase of an e-commerce company.
After this acquisition, the future of the eCommerce industry in India has become more competitive than ever.
The three main reasons for the acquisition of Flipkart are Flipkart’s leadership in some lucrative sections, its payment platform, and the company’s talent pool.
Here are some key outcomes of Walmart's acquisition of Flipkart:
- Market Entry: The acquisition allowed Walmart to enter India’s growing eCommerce market, which is expected to be one of the largest in the world. Flipkart has a strong presence, with over 200 million registered users and a wide range of products.
- Competing with Amazon: Walmart’s acquisition of Flipkart was a strategic move to compete with Amazon, which is rapidly growing in India. This acquisition gives Walmart a strong position in the Indian eCommerce market.
- Technological Advancement: Flipkart’s advanced technology and eCommerce expertise have helped Walmart improve its online services. Flipkart offers features like mobile payments, personalized recommendations, and data analytics, enhancing Walmart’s customer engagement.
- Supply Chain Improvement: By using Flipkart’s strong supply chain and logistics in India, Walmart has improved its delivery and fulfillment operations. This has made their logistics more efficient.
Walmart, the world’s largest company, continues to expand its business by improving its strategies every day. The main reason for the success of Walmart is the EDLP system, i.e., Everyday Low Price. They are working aggressively to maintain profits, market shares, and provide low prices to consumers. There are many business ideas to gain profit from a market. It all depends on how you play the cards for a profitable business.
Walmart has made acquisitions of 28 organizations and has 16 sub-organizations.
 StartupTalkyKinnary Nensee
StartupTalkyKinnary Nensee
Walmart Controversies
Walmart has below controversies attached to it:
- In recent years, Walmart has faced accusations of mistreating workers and paying low wages, with many employees saying they have bad working conditions and not enough pay.
- The company has also dealt with legal problems, including a big gender discrimination lawsuit from 2001 that was settled for $11 million.
- Walmart's low prices and aggressive pricing strategies have been criticized for putting small businesses out of business and harming traditional shopping areas in many communities.
Walmart SWOT Analysis
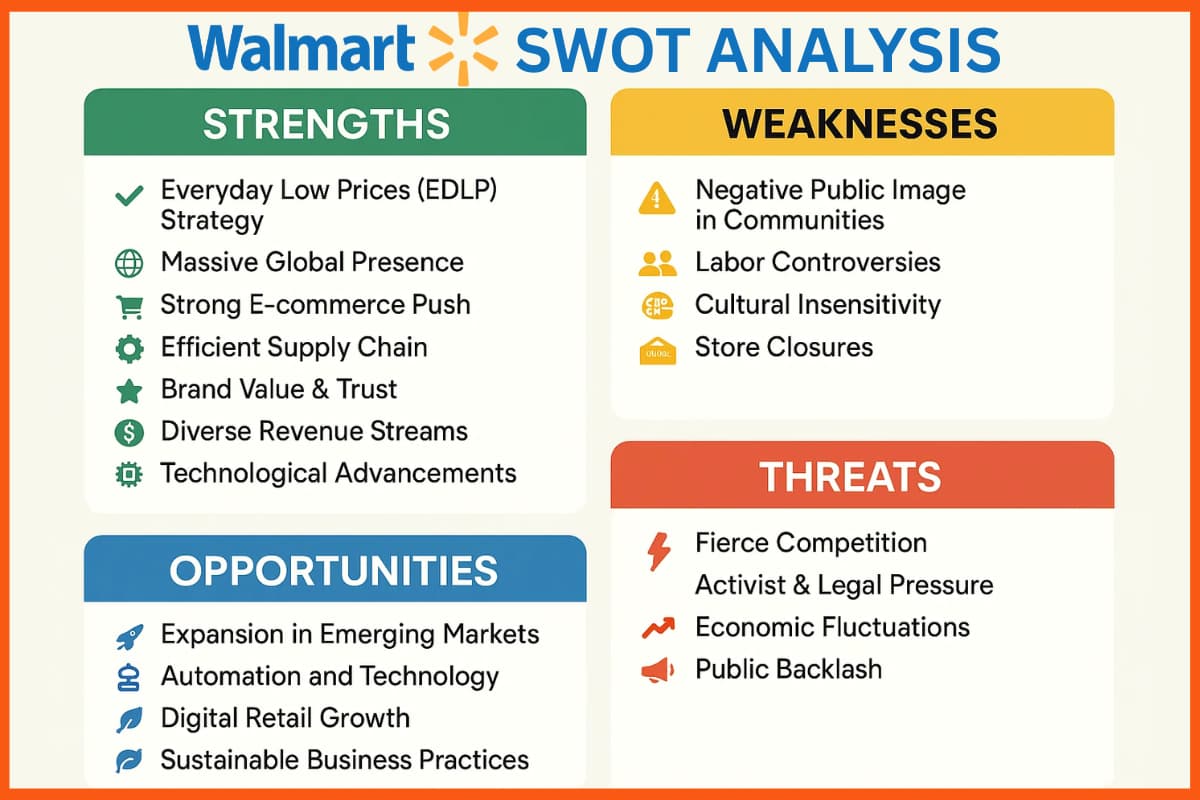
Strengths
- Everyday Low Prices (EDLP) Strategy: Strong pricing advantage attracts cost-conscious shoppers.
- Massive Global Presence: Operates thousands of stores worldwide across various formats.
- Strong E-commerce Push: Acquisitions like Jet.com and Flipkart boosted digital reach.
- Efficient Supply Chain: Advanced logistics and bulk buying reduce costs.
- Brand Value & Trust: One of the most recognized and valuable retail brands globally.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: Earns from both product and service segments.
- Technological Advancements: Investments in AI, robotics, and data analytics enhance operations.
Weaknesses
- Negative Public Image in Communities: Seen as harmful to small merchants and local businesses.
- Labor Controversies: Allegations of low wages, poor working conditions, and legal issues like discrimination.
- Cultural Insensitivity: Accusations of not respecting local culture or languages in new markets.
- Store Closures: Failed expansions in countries like Germany and Louisiana hurt global strategy.
Opportunities
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: India and other developing nations present strong growth potential.
- Automation and Technology: Increased automation can cut costs and improve efficiency.
- Digital Retail Growth: Rise in online shopping offers huge scope for Walmart+ and e-commerce operations.
- Sustainable Business Practices: More focus on environmental campaigns can improve public perception.
Threats
- Fierce Competition: Faces stiff competition from Amazon and local retailers worldwide.
- Activist & Legal Pressure: Increasing resistance from activists and lawsuits may affect growth.
- Economic Fluctuations: Inflation, supply chain issues, or recessions can reduce consumer spending.
- Public Backlash: Continued criticism for harming small businesses and communities may affect the reputation.
Walmart Future
By the end of Fiscal Year 2026, Walmart expects that around 65% of its stores will utilize automation, with about 55% of fulfillment center operations transitioning to automated facilities. Additionally, the company anticipates a potential 20% improvement in unit cost averages.
FAQ's
What is the business model of Walmart?
The business model of Walmart is based on eliminating the middleman from the distribution channels. The advantage of removing the middleman is to provide benefits to the consumer by providing products at lower costs.
What is the motive behind Walmart's Business Strategy?
The main motive of the Walmart business strategy company is to enter every segment of the market and dominate the market by providing products at a lower price.
What is Walmart's Market Strategy?
The company follows cost leadership which makes a huge profit for the company. The company provides low prices to the consumer and treats all the customers as king of the market to maintain the relationship between Walmart and the customer.
How does Walmart generate revenue?
The earning model of Walmart deals with the principle of buying in bulk in one go. In this system, they got a huge discount from the manufacturers. Walmart generates its revenue by removing the middleman and selling its products directly to the customers and services to businesses.
What are the main sources of revenue for Walmart?
The two main sources of revenue are:
- Product revenue
- Service revenue
Is Walmart owned by China?
The Walmart branch in China is majority Chinese-owned. But predominantly it is owned by Sam Walton's many children.
Why is Walmart so cheap?
They sell in small quantities at low prices. By reducing the price they have high sales volume through which they have high earnings. Hence, by selling in high volume they can sell it at a cheap price and still gain profit.
What are the sub-organisations under Walmart?
There are 16 sub-organisations of Walmart. Some of them are:
- Walmart Labs
- Seiyu Group
- Walmart Canada
- Sam's Club
- Mas Club
- Lider
- Vudu
What are the top acquisitions of Walmart?
Walmart has acquired 28 companies. Some top acquisitions are:
- Flipkart
- Thunder
- Art.com
- Botmock
- MeMD
- Polymorph
- Aspectiva
Identify the major factors contributing to the success of Walmart in tough times?
Walmart’s success in tough times is driven by its Everyday Low Prices strategy, strong supply chain, and ability to adapt quickly. Its scale allows bulk purchasing, keeping prices low, while investments in e-commerce, automation, and data analytics boost efficiency. Local sourcing and a wide product range also help maintain customer loyalty.
Original Article
(Disclaimer – This post is auto-fetched from publicly available RSS feeds. Original source: Startuptalky. All rights belong to the respective publisher.)